Per què triar-nos
- Excel·lència mèdica
- Equip especialitzat
- Líders en Investigació
- Atenció personalitzada
Excel·lència mèdica i honestedat en un equip vinculat a investigacions de primer nivell internacional
Amb empatia i rigor, els professionals de l’Institut de la Màcula apliquem els tractaments més innovadors i posem sempre per davant els interessos dels pacients. Tenim com a principi no forçar mai cap indicació.
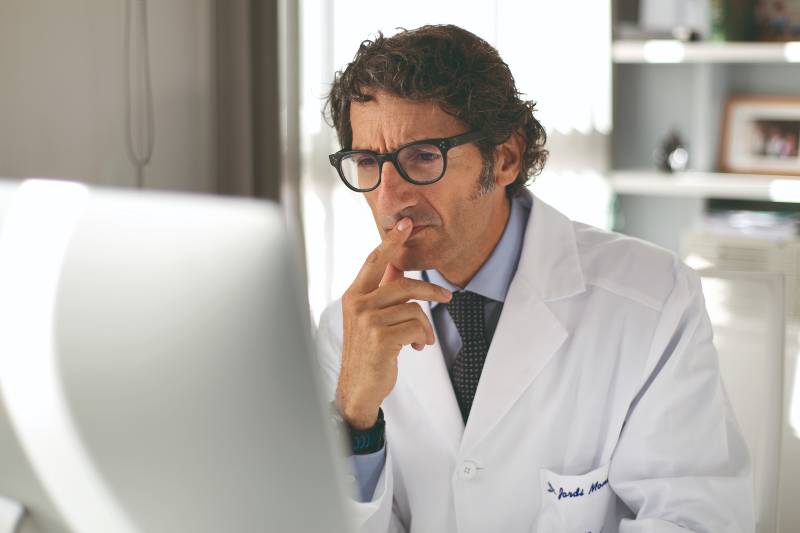

Professionals altament especialitzats, amb experiència clínica i qualitat humana
L’equip de l’Institut de la Màcula està en constant actualització, pendent de les tècniques més avançades i de les aportacions acadèmiques més rellevants provinents de tot el món. Oferim als nostres pacients la millor assistència possible amb rigor, professionalitat i calidesa.
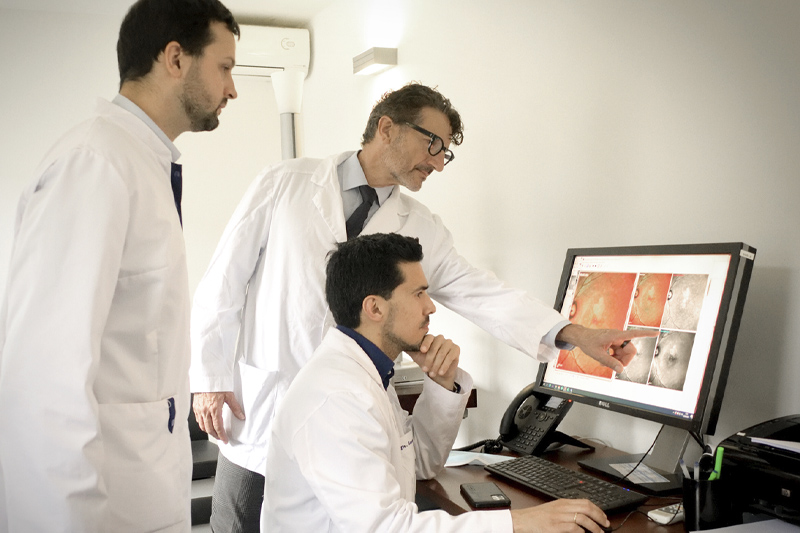

Liderem investigacions de referència a tot el món
Treballem en xarxa amb institucions de referència internacional per tirar endavant projectes innovadors en investigació clínica. Així podem oferir, als pacients que compleixen els criteris d’inclusió, l’accés a estudis i assajos clínics per a patologies que encara no tenen tractament.
Estudiem cas per cas, sense apriorismes ni cap altre interès que el benestar del pacient
Fem prescripcions ajustades, sense sobremedicació, i només intervenim quan és necessari.
Dediquem a cada pacient el temps que es mereix, sense presses. Atenem amb empatia i ens interessem tant pels símptomes com per les circumstàncies de cada persona.
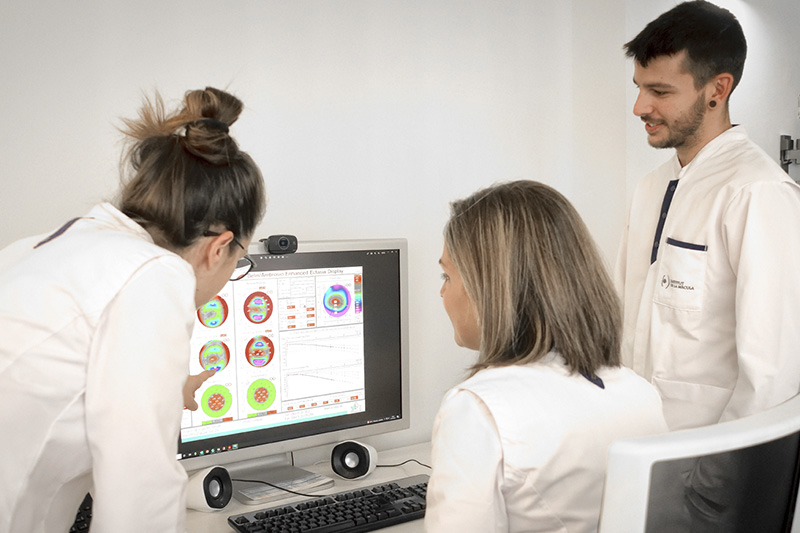

Volem que segueixis veient les coses bones de la vida
Perquè la bellesa està en els detalls i val la pena gaudir-los tots
Posem tot el nostre esforç a frenar la pèrdua visual. La nostra vocació és aconseguir un futur sense ceguesa i aconseguir que els nostres pacients es beneficiïn quan abans dels resultats de les investigacions més avançades.
Els nostres compromisos
Vocació, vincle amb pacients i famílies, rigor científic i honestedat en la prescripció.
Els nostres diagnòstics i tractaments estan basats en l’evidència científica i sempre posem la persona per davant, sense cap altre interès ni objectiu que el seu benestar físic i emocional.
EXCEL·LÈNCIA MÈDICA
És el criteri amb què seleccionem els professionals que formen part del nostre equip.
EMPATIA I QUALITAT HUMANA
Ens apropem a la persona amb comprensió i vocació d’acompanyament integral.
ATENCIÓ PERSONALITZADA
Fugim de tractaments predefinits. Busquem sempre el millor per a cada persona.
INVESTIGACIÓ
La nostra vocació científica ens porta a col·laborar amb les millors institucions del món.
Els nostres compromisos
Vocació, vincle amb pacients i famílies, rigor científic i honestedat en la prescripció.
Els nostres diagnòstics i tractaments estan basats en l’evidència científica i sempre posem la persona per davant, sense cap altre interès ni objectiu que el seu benestar físic i emocional.
EXCEL·LÈNCIA MÈDICA
EMPATIA I QUALITAT HUMANA
ATENCIÓ PERSONALITZADA
INVESTIGACIÓ
Què opinen els nostres pacients?
Subscriu-te al nostre newsletter digital
Ens comprometem a enviar-vos només informació rellevant i no compartir el vostre contacte.